1-What glass is fire resistant glass?
According to Safety Glass for Buildings – Part 1: Fire-resistant Glass (GB 15763.1-2009), Clause 4.1, the classification is as follows:
- By structure: Composite Fire-resistant Glass (FFB) and Monolithic Fire-resistant Glass (DFB).
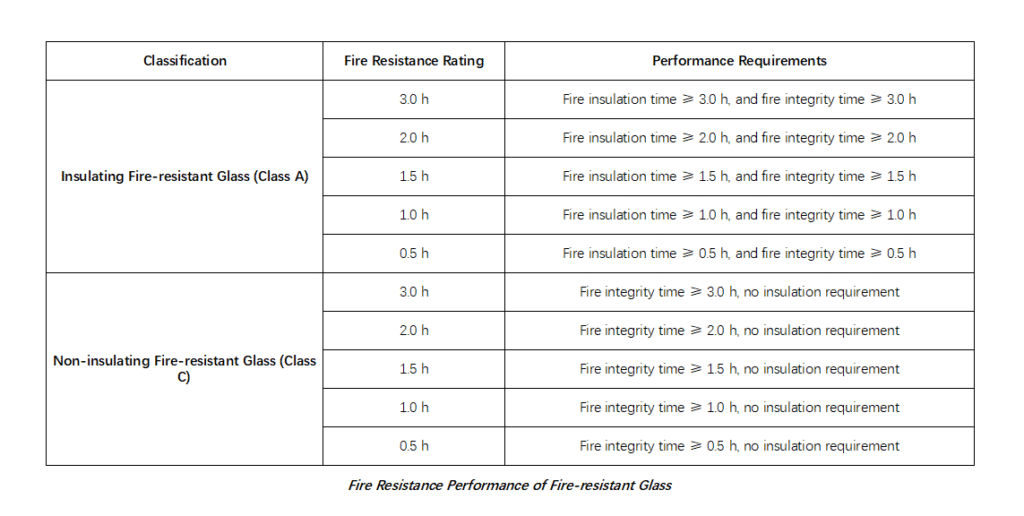
- By fire-resistance performance: Insulating type (Class A) and Non-insulating type (Class C).
- By fire-resistance rating: Five levels — 0.5 h, 1.00 h, 1.50 h, 2.00 h, and 3.00 h.
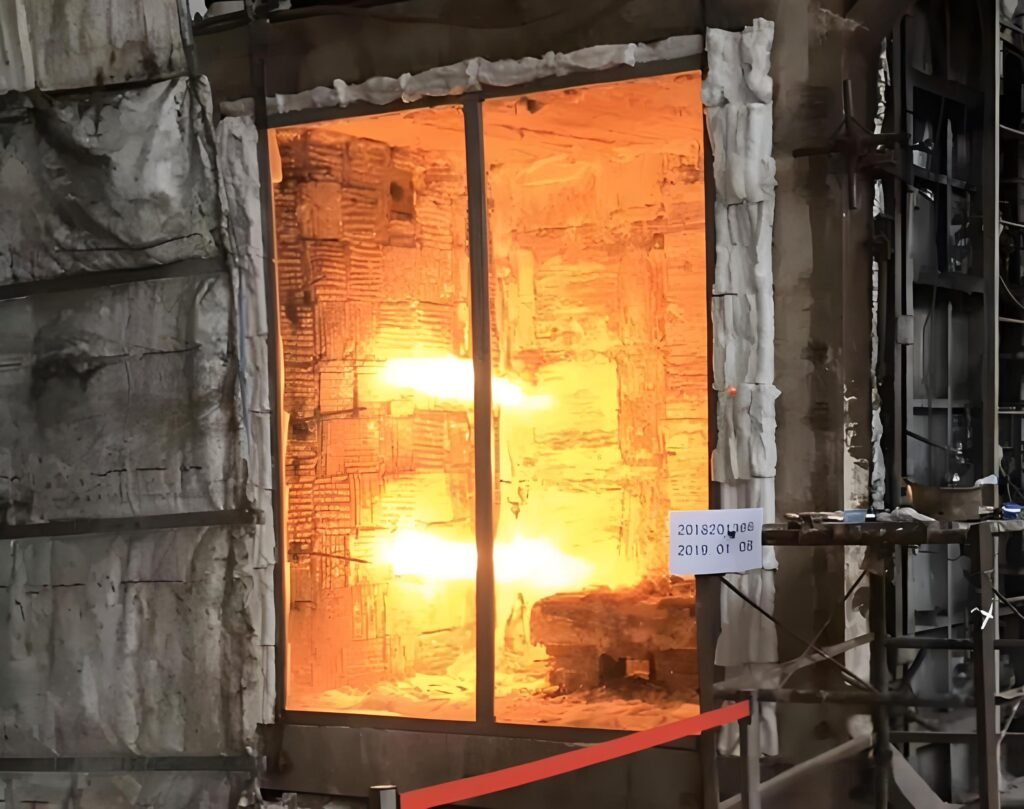

Fire-resistance performance of fire-resistant glass
- Insulating fire resistant Glass (Class A) – Fire-resistant glass that simultaneously meets the requirements of fire integrity and thermal insulation.
- Non-insulating fire-resistant Glass (Class C) – Fire-resistant glass that only meets the requirement of fire integrity.
Fire integrity – Under standard fire test conditions, the ability of a glass component, when exposed to fire on one side, to prevent flames and hot gases from penetrating or flames appearing on the unexposed side for a specified period of time.
Thermal insulation – Under standard fire test conditions, the ability of a glass component, when exposed to fire on one side, to ensure that the temperature rise on the unexposed surface does not exceed the prescribed limit for a specified period of time.
Fire-resistance rating – Under standard fire test conditions, the duration from the moment a glass component is exposed to fire until it loses either fire integrity or thermal insulation performance.
2-What is High Borosilicate Fireproof Glass?
Borosilicate fire proof glass is a widely used type of safety glass known for its low thermal expansion coefficient and excellent resistance to thermal shock.
Chemical Composition of Borosilicate Fireproof Glass
The typical composition includes:
- SiO₂ (Silicon Dioxide): 68% – 78%
- B₂O₃ (Boron Trioxide): 10% – 13%
- Al₂O₃ (Aluminum Oxide): 2% – 4%
- R₂O (Alkali Oxides): 4% – 8%
Features of High Borosilicate Fireproof Glass
High borosilicate fireproof glass is an advanced product developed in recent years. It is manufactured from high-purity borosilicate raw glass through a special toughening process, making it a fully tempered, non-insulating single-pane fire-resistant glass. Unlike conventional cesium-potassium fireproof glass, high borosilicate glass offers superior safety and performance.
- Tested thicknesses of high borosilicate glass achieve a fire resistance rating of up to 3 hours, compared to only 1 hour for single-pane cesium-potassium fireproof glass, which is less stable.
- With a boron content of 12.5–13.5% and silicon content of 78–80%, the glass demonstrates excellent acid and alkali resistance, withstands thermal differences up to 520°C, endures continuous exposure to 750°C without degradation, and has a softening point above 850°C.

Key Performance Advantages of High Borosilicate Fireproof Glass
No homogenization required – stable, no crystallization, no spontaneous breakage.
Low-iron glass – clearer, more aesthetically pleasing.
The only single-pane fireproof glass suitable for water sprinkler systems.
Durable chemical stability – resistant to acids, alkalis, and UV radiation; suitable for both indoor and outdoor use without discoloration or deformation.
Long fire resistance time – ≥ 3 hours certified by authoritative testing.
3-What is laminated fire-resistant glass
Composite fire-resistant glass (excellent fire resistance performance)
Composition:
It is made by laminating two or more sheets of glass with one or more layers of water-soluble inorganic fire-resistant interlayer adhesive.
Fire-resistance principle:
When a fire occurs, the glass on the fire-exposed side quickly cracks under high temperatures. The fire-resistant interlayer then begins to foam and expand—by approximately ten times its original thickness—forming a rigid, opaque, milky-white fireproof barrier. This layer effectively blocks flames and prevents the spread of heat and toxic gases. The finished glass can be edge-ground, drilled, and cut to size.
Applications:
When used in exterior windows or curtain walls, the design should consider combining fire proof glass with PVB laminated glass.
Applicable for fire-rated doors and windows, fire partitions in rooms, corridors, and passageways, as well as fire-resistant walls in critical areas of buildings.
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Composition | Composed of two or more sheets of glass laminated with one or more layers of water-soluble inorganic fire-resistant interlayer adhesive. |
| Fire-Resistance Principle | When a fire occurs, the glass on the fire-exposed side quickly cracks under high temperatures. The fire-resistant interlayer then foams and expands—by about ten times—forming a rigid, opaque, milky-white fireproof barrier that effectively blocks flames and isolates heat and toxic gases. |
| Processing Properties | The finished glass can be edge-ground, drilled, and cut to size. |
| Design Recommendation | When used for exterior windows or curtain walls, the design should consider combining fire-resistant glass with PVB laminated glass. |
| Applications | Suitable for fire-rated doors and windows, fire partitions in rooms, corridors, and passageways, as well as fire-resistant walls in key areas of buildings. |
Gel-filled fire-resistant glass (superior thermal insulation performance)
Composition:
Made from two sheets of float glass (or three sheets if specially required), sealed around the edges with a specially formulated flame-retardant sealing strip. The cavity between the glass sheets is filled with a fire-resistant gel, which cures into a transparent, jelly-like layer firmly bonded to the glass to form an integral unit.
Fire Resistance Principle:
When exposed to high temperatures, the transparent gel layer between the glass sheets rapidly solidifies into an opaque fire-resistant and heat-insulating barrier. This layer not only prevents the spread of flames but also blocks heat transfer to the non-fire side. Such fire-resistant glass provides both fire and thermal insulation performance, as well as excellent sound insulation. It can also be processed into curved shapes.
Applications:
Ideal for fire-rated doors and windows, atriums, skylights, shared spaces, and fire partitions in areas such as computer rooms and building courtyards.
Note:
Chemical gel-filled fire-resistant glass tends to form air bubbles during production. Under ultraviolet radiation or direct flame exposure, it quickly turns milky white, losing its essential transparency and thereby preventing visibility through the glass during a fire.

4-Comprehensive guide to selecting fire proof glass for buildings: types, applications, and standards
Detailed content
1. Understand fire safety requirements first
Before selecting fire proof glass, clearly define the fire system requirements:
- Heat insulation or non-heat insulation needs
- Fire-resistance rating
- Glass panel dimensions
2. Consider supporting structures and materials
The fire performance of glass depends not only on the glass itself but also on its supporting structure and components. All materials used must meet relevant national and industry standards as well as technical specifications.
3. System-based approach Is essential
Do not simply replace ordinary glass or non-fire-rated materials in curtain walls or partitions with fire-resistant glass. The overall fire-resistance performance of the system must be evaluated. Testing may be required to ensure compliance with fire-safety standards.
4. Cutting and processing requirements
- Single-pane and gel-filled fire-resistant glass cannot be cut like ordinary flat glass and must be fabricated to precise dimensions.
- Dry-laminated composite fire-resistant glass can be cut as needed.
5. Heat-insulating fire-resistant glass (Class A)
- Typically uses composite fire rate glass or gel-filled (injection-type) fire-resistant glass.
- When used on exterior walls, long-term exposure may cause bubbles or yellowing, affecting appearance.
6. Non-heat-insulating fire-resistant glass (Class C)
- Usually uses single-pane fire proof glass.
- Features: high light transmittance, fire resistance, smoke isolation, and high strength.
- Suitable for: non-heat-insulated fire partitions, fire-rated windows, and exterior curtain walls.
5-How fire proof glass substrates I can use?
Types of glass substrates:
- Float glass (coated or uncoated)
- Tempered glass
- Composite fire-resistant glass substrates
- Single-pane fire-resistant glass
Standards compliance:
Each glass substrate shall comply with relevant international standards or Chinese standards, as well as the specific provisions outlined in this section.
Protect Your Building with the Right Fire Poof Glass Today
Ensure safety, compliance, and aesthetic quality by selecting the appropriate fire-resistant glazing for your project. Whether you need single-pane, composite, or gel-filled fire-resistant glazing, our expert guidance and high-quality products meet all international and Chinese standards.
Contact us now to discuss your project requirements and get a tailored fire-resistant glass solution that combines safety, performance, and design flexibility.